- Home
- About Us
Suzhou East Railway Co., Ltd. is a railway specialist supplier with the core vision of providing railway vehicles and components for passenger cars and freight wagons, project management and maintenance services.
China has the most complete railway products in the world and mature technology, has Enough railway products for customer selection.
Marketing »Rail operators or private miners are one of our main customers,and the range of requirements is usually very wide and the requirements are very high.
- Products
- Passenger Car
- ● Coach
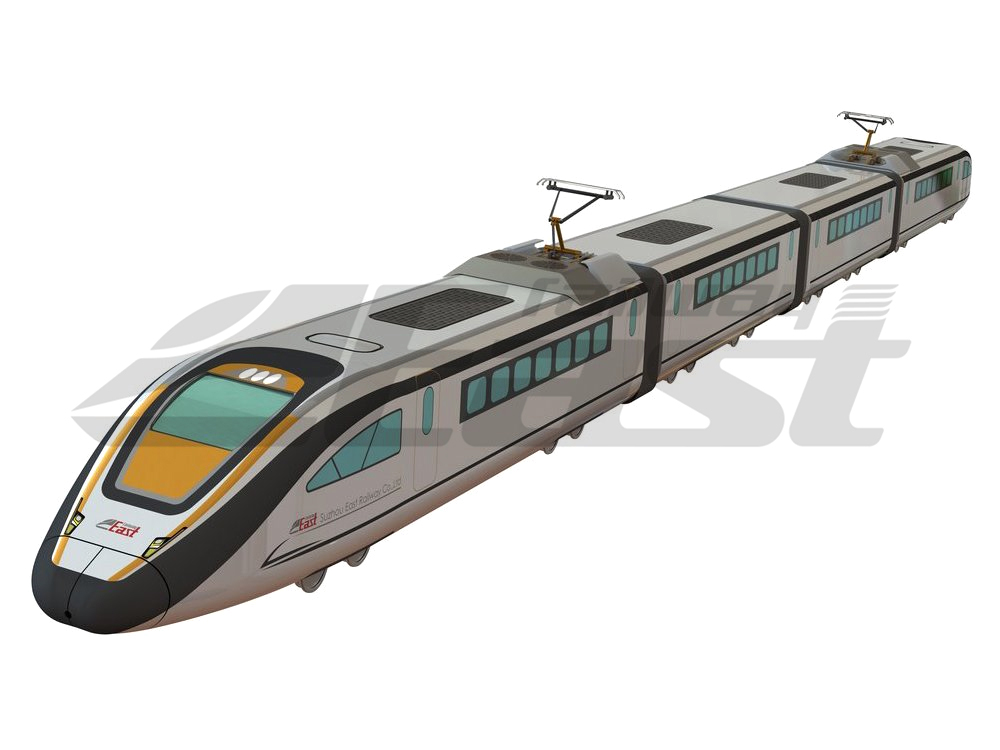
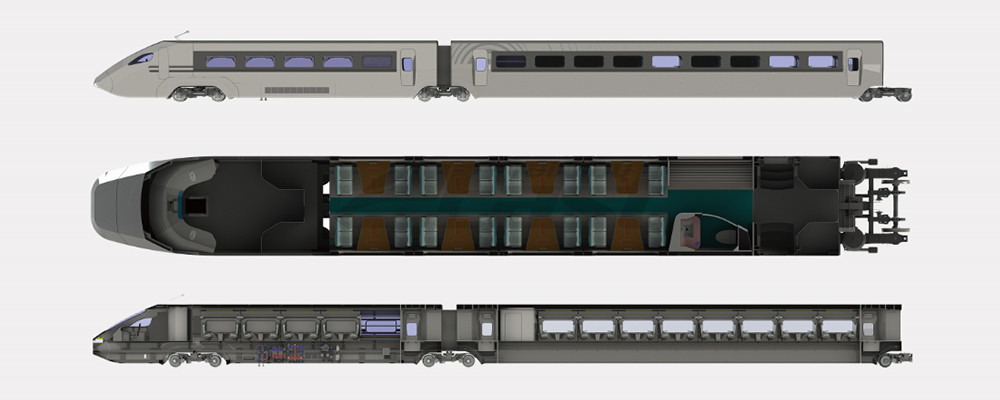
- ● EMU&DMU
- ● LRT
- ● Metro
- ● Monorail
- ● Tram
- Freight Wagon
- ● Covered Wagon
- ● Open-top Wagon
- ● Tank Wagon
- ● Flat Wagon
- ● Hopper Wagon
- Module
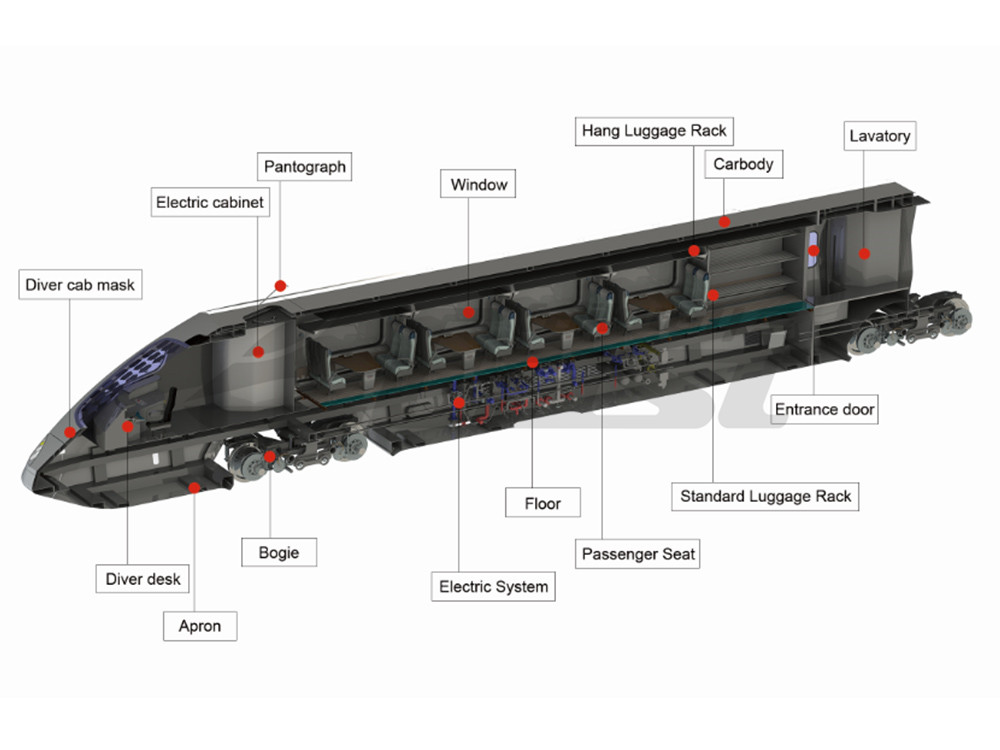
- ● Bogie
- ● Carbody
- ● Interior-Passenger Car
- ● Interior-Driver Cabin
- ● Interior-Toilet
- System
- ● Passenger Information System
- ● Toilet System
- ● Air Conditioning System
- ● Lamp System
- ● Gangway Diaphragm
- ● Draft Gear System
- Passenger Car Spare Parts
- ● Railway Door Leaf
- ● Railway Seat
- ● GFRP-Interior Panel
- ● Luggage Rack
- ● Railway Window
- ● Sheet Metal
- Freight Wagon Spare Parts
- ● Air Brake System
- ● Brake Beam Device
- ● Wheel Set
- ● Spring
- ● Side Bearing
- ● Wearing Parts
- ● Casting And Forging Parts
Railway Vehicle » Module And System »
Module And System » Vehicle Spare Parts »
Vehicle Spare Parts » Renovation And Maintenance »East Railway have the ability to refurbish or upgrade railway vehicles (wagon/passenger cars) ,including mechanical,interior and electrical system of any type of passenger car and freight wagon.East Railway is committed to safety,quality and efficiency,we can provide the knowledge and skills that you require.
Renovation And Maintenance »East Railway have the ability to refurbish or upgrade railway vehicles (wagon/passenger cars) ,including mechanical,interior and electrical system of any type of passenger car and freight wagon.East Railway is committed to safety,quality and efficiency,we can provide the knowledge and skills that you require.
- Service
We can participate in and assist you in the calibration of the product from the beginning of the rail transit project planning and provide you with a suitable vehicle……
Rail transit industry projects, especially vehicle projects, are usually immense in size and very complex, therefore requiring professional support and control……
If you are in the country or region of the rail transit bidding project, you have considerable bidding convenience or ability, but need technical or supply……
If you are engaged in the rail vehicle products industry or have railway customers in the local or surrounding area.You can apply as an agent of East Railway……
After-sales Service »No matter what kind of products or services you choose, East Railway will provide you with corresponding after-sales service. East Railway’s services are continuous and improvement. We base ourselves on building long-term and in-depth cooperation between East Railway and our customers.
- Media
- Contact Us
 +86-13438615686
+86-13438615686
 faith@eastrailway.com
faith@eastrailway.com